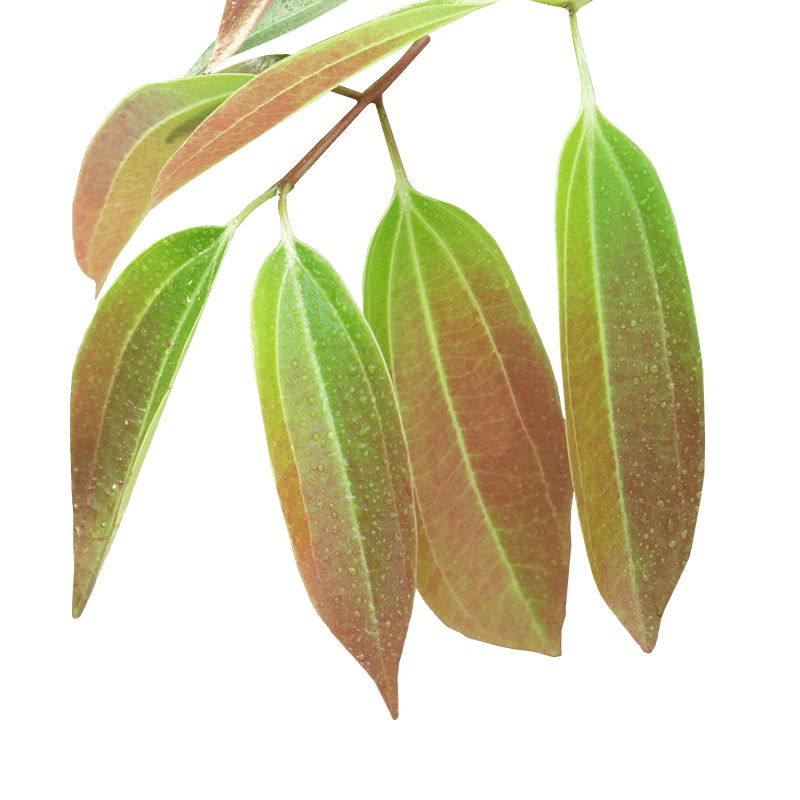

Cinnamomum aromaticum or cassia
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Essential oil (cinnamaldehyde): stimulates the appetite and digestion and has a carminative and spasmolytic effect. It is also antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal.
Tannins (OPC): have an antioxidant and glucose-lowering action.
Usage
Cinnamon is a warming spice, well known in oriental cuisine, but it has also been used for thousands of years in traditional phytotherapy. Cinnamon-based preparations are used to treat anorexia, bloating, nausea, dyspepsia, colic and intestinal cramps. Thanks to its antiseptic properties, it is also used as an ingredient in toothpaste. Essential oil is used in certain perfumes and liqueurs. Cinnamon stimulates the appetite, improves the digestion of fats and is involved in carbohydrate metabolism. It contributes to digestive comfort. 1-6 It has stimulating properties that contribute to resistance to mental and physical fatigue. 7.8
Bibliographical references
- Antifoaming and carminative actions of volatile oils
Harries N, James KC, Pugh WK.
Journal of clinical pharmacology, 1978, 2:171–177.
Wiley Online Library: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2710.1977.tb00087.x/abstract - Relaxant effects on tracheal and ileal smooth muscles of the guinea pig.
Reiter M, Brandt W.
Arzneimittelforschung. 1985;35(1A):408-14.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4039178 - Effects Of Carminative Volatile Oils On The Muscular Activity Of The Stomach And Colon
O. H. Plant, G. H. Miller
J Pharmacol Exp Ther March 1926 27:149-164
Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics: http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/27/2/149.abstract - Pharmacological studies on Chinese cinammon. II. Effects of cinnamaldehyde on the cardiovascular and digestive systems.
Harada M, Yano S.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1975 May;23(5):941-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1181070 - Additive postprandial blood glucose-attenuating and satiety-enhancing effect of cinnamon and acetic acid.
Mettler S, Schwarz I, Colombani PC.
Nutr Res. 2009 Oct;29(10):723-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19917452 - Nutritional, dietary and postprandial oxidative stress.
Sies H, Stahl W, Sevanian A.
J Nutr. 2005 May;135(5):969-72.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15867266 - Pharmacological studies on Chinese cinnamon. V. Catecholamine releasing effect of cinnamaldehyde in dogs.
Harada M, Hirayama Y, Yamazaki R.
J Pharmacobiodyn. 1982 Aug;5(8):539-46.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6130136 - TRPA1 agonists--allyl isothiocyanate and cinnamaldehyde--induce adrenaline secretion.
Iwasaki Y, Tanabe M, Kobata K, Watanabe T.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008 Oct;72(10):2608-14.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18838811
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).
 Belgium
Belgium
 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος 