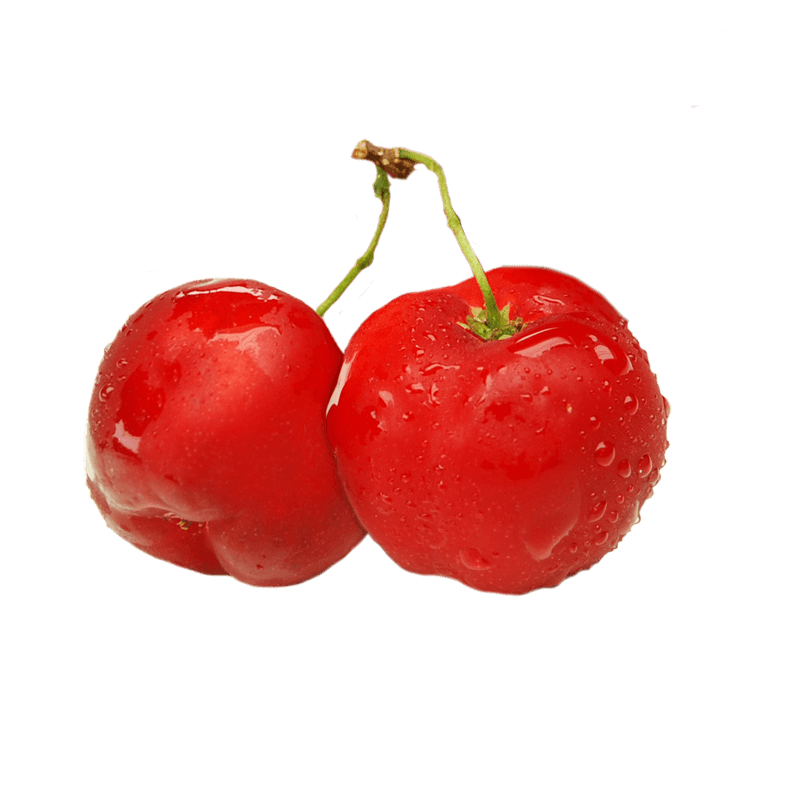
Barbados cherry
Latin name
Origin
Used part
Active components
Usage
Bibliographical references
- Absorption and excretion of ascorbic acid alone and in acerola(Malpighia emarginata) juice: comparison in healthy Japanesesubjects.
Uchida E, Kondo Y, Amano A, Aizawa S, Hanamura T, Aoki H,Nagamine K, Koizumi T, Maruyama N, Ishigami A.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(11):1744-7.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22040889
- [The acerola fruit: composition, productivecharacteristics and economic importance].
Mezadri T, Fernández-Pachón MS, Villaño D, García-ParrillaMC, Troncoso AM.Pubmed:
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17024954
Arch Latinoam Nutr. 2006 Jun;56(2):101-9.
- Vitamin C as an Antioxidant: Evaluation of Its Role inDisease Prevention
Sebastian J. Padayatty, MRCP, PhD, Arie Katz, MD, YaohuiWang, MD, Peter Eck, PhD, Oran Kwon, PhD, Je-Hyuk Lee, PhD,Shenglin Chen, PhD, Christopher Corpe, PhD, Anand Dutta, BS, SudhirK Dutta, MD, FACN and Mark Levine, MD, FACN
J Am Coll Nutr February 2003 vol. 22 no. 1 18-35
Journal of the American College of Nutrition:http://www.jacn.org/content/22/1/18.full
- Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold.
Douglas RM, Hemila H, D'Souza R, Chalker EB, Treacy B.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD000980.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15495002
- The role of vitamin C in iron absorption.
Hallberg L, Brune M, Rossander L.
Int J Vitam Nutr Res Suppl. 1989;30:103-8.
Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2507689
The health claims that feature on our website in relation to the plants contained in our products are compliant with the list of health claims awaiting final assessment by the Community authorities (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/). However, they may be subject to modification following their assessment by the national competent authorities.
The health claims relating to other nutrients or substances contained in our products that feature on our site are compliant with Regulation No. 432/2012 of the Commission of 16 May 2012 which establishes a list of authorised health claims authorised in relation to food products, other than those in reference to the reduction of the risk of disease as well as community-based development and child health (cf. website of the European Commission: http://ec.europa.eu/nuhclaims/).

 Belgique
Belgique  België
België  France
France  Italia
Italia  Portugal
Portugal  España
España  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Κύπρος
Κύπρος